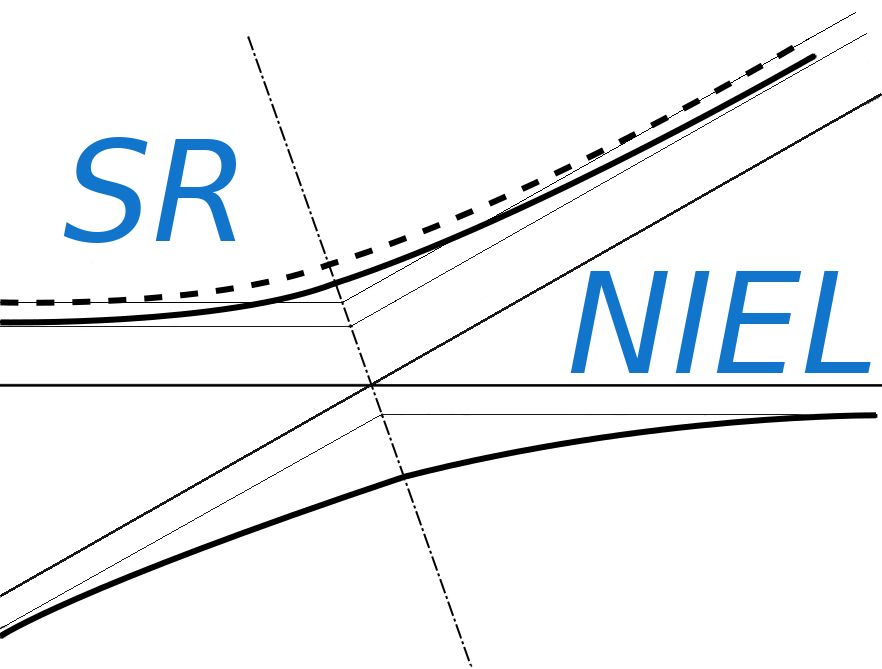
Figure 1 shows the maximum percentage difference in the damage functions obtained with NJOY-2021 (version 1.2.2) with respect NJOY-2016 (version 65) when ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library is employed.
 Figure 1. Maximum percentage difference of damage function obtained with NJOY-2021 with respect NJOY-2016 as a function of the target element using both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition functions. ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library is employed.
Figure 1. Maximum percentage difference of damage function obtained with NJOY-2021 with respect NJOY-2016 as a function of the target element using both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition functions. ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library is employed.
For almost all target elements there is no difference in the values obtained with NJOY-2021 with respect NJOY-2016, only for Oxigen there is a negligible difference.
Differences in damage function arise when ENDF/B.VIII.0 or ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library are employed.
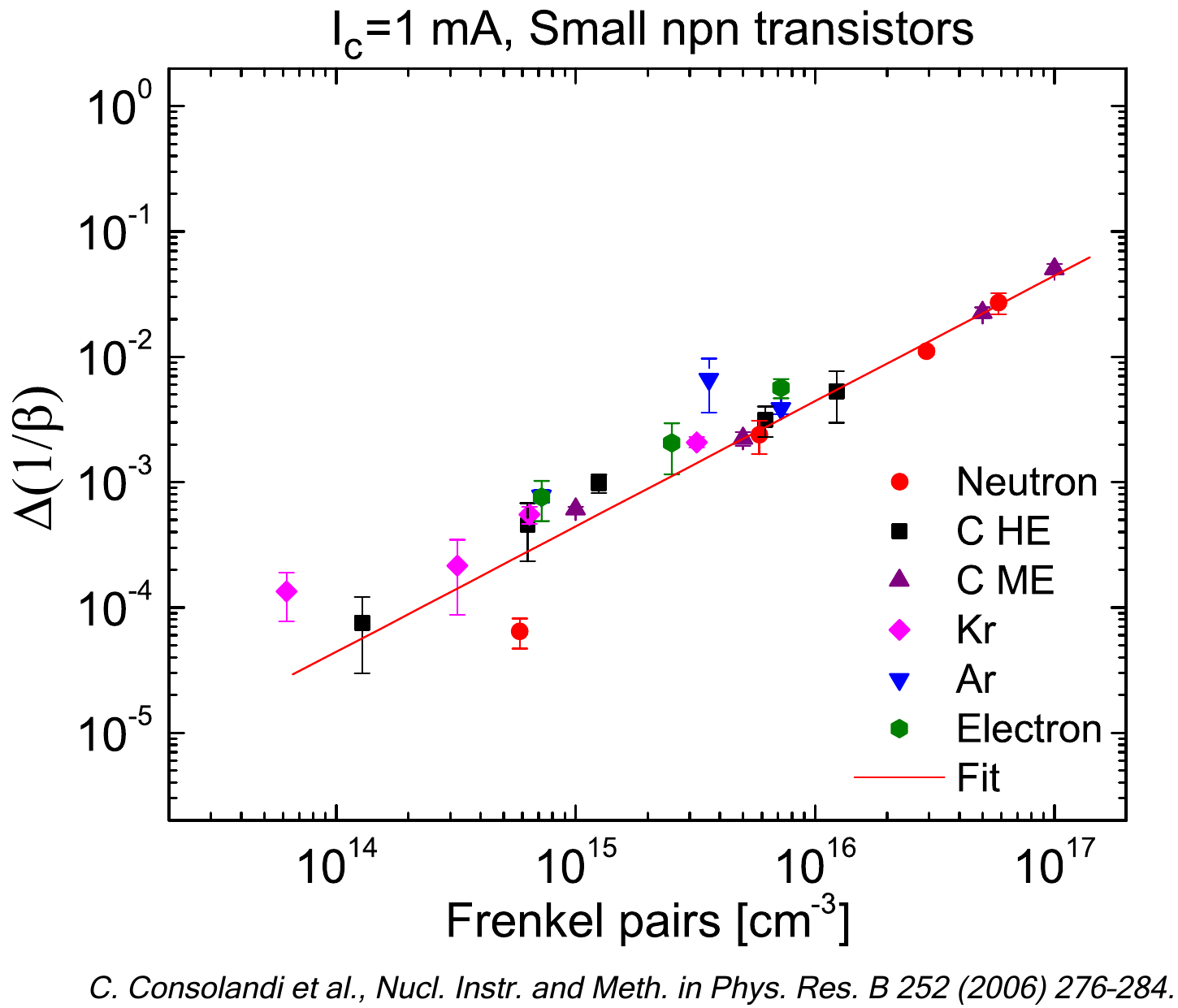
The following figures show the percentage difference in the neutron NIEL dose employing NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The reactor spectral fluences are those of ITN-ΣΣ (from [Angelescu et al. (1994)]), IPEN/MB-01 (from [Bitelli et al. (2009)]), TRIGA-Vienna (from [Cagnazzo (2014)]), TRIGA ENEA Casaccia and TAPIRO ENEA Casaccia. TRIGA ENEA spectrum is measured at 100 kW in the Lazy Susan channel. TAPIRO ENEA spectrum is measured at 4 kW in the Radial channel 1.
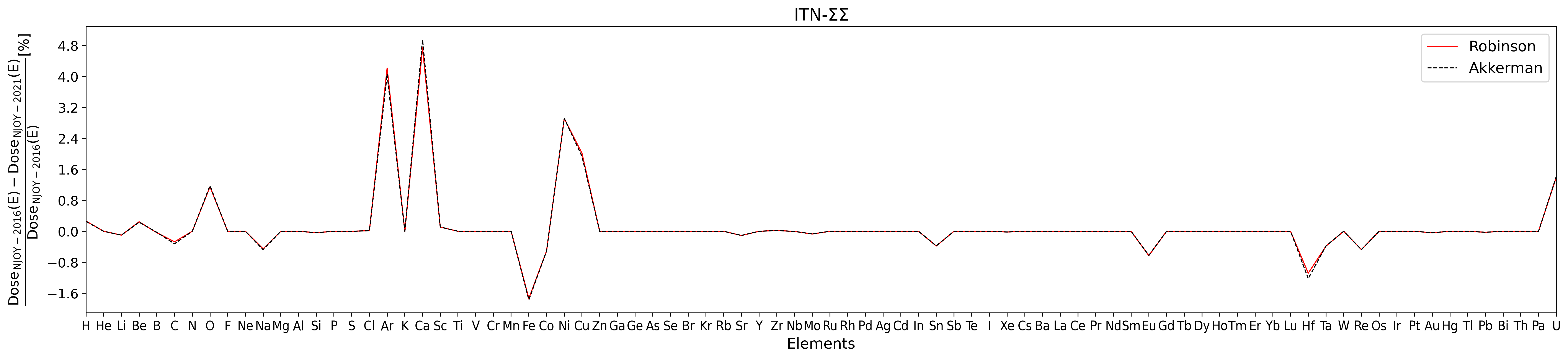 Figure 2. NIEL Dose percentage difference for ITN-ΣΣ (from [Angelescu et al. (1994)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
Figure 2. NIEL Dose percentage difference for ITN-ΣΣ (from [Angelescu et al. (1994)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
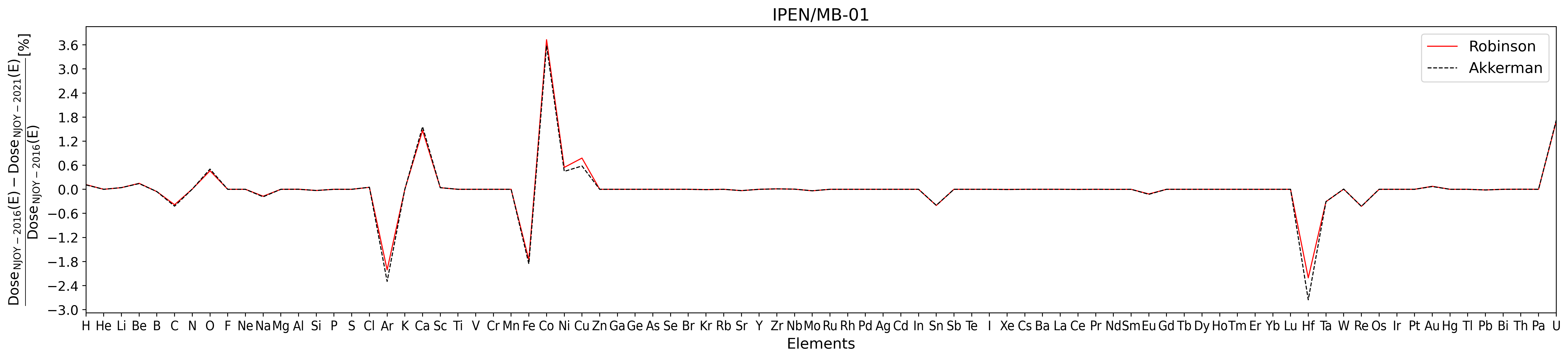 Figure 3. NIEL Dose percentage difference for IPEN/MB-01 (from [Bitelli et al. (2009)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
Figure 3. NIEL Dose percentage difference for IPEN/MB-01 (from [Bitelli et al. (2009)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
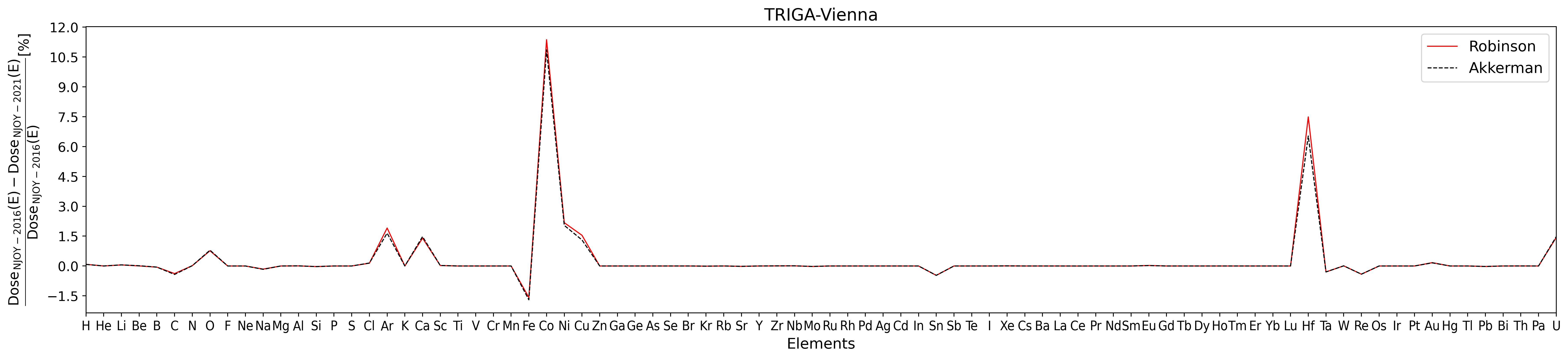 Figure 4. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TRIGA-Vienna (from [Cagnazzo (2014)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
Figure 4. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TRIGA-Vienna (from [Cagnazzo (2014)]) spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
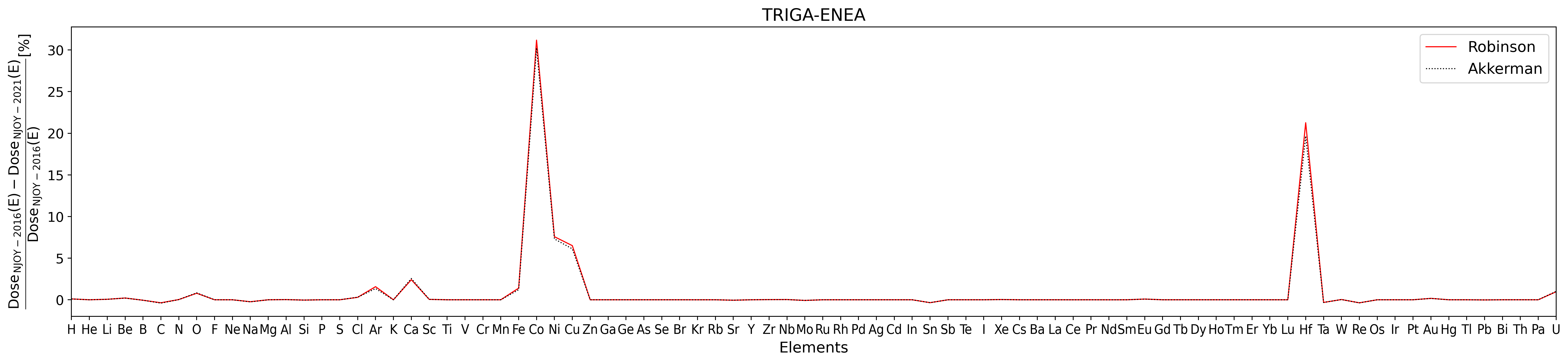 Figure 5. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TRIGA ENEA Casaccia spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
Figure 5. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TRIGA ENEA Casaccia spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
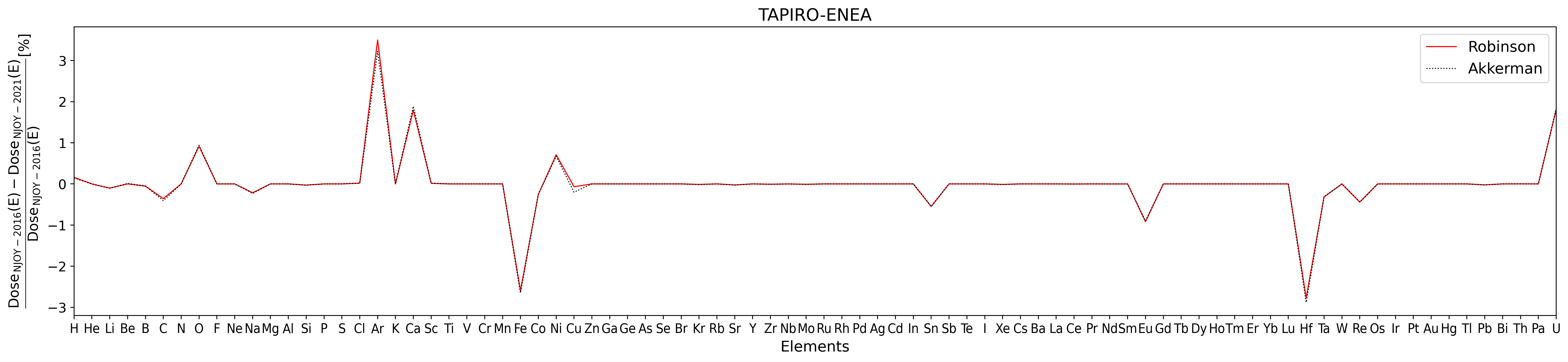 Figure 6. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TAPIRO ENEA Casaccia spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
Figure 6. NIEL Dose percentage difference for TAPIRO ENEA Casaccia spectral fluence as a function of target elements for NJOY-2021 using ENDF/B.VIII.0 cross section library with respect NJOY-2016 using ENDF/B.VII.1 cross section library. The analysis is performed for both Robinson (solid red line) and Akkermann (dashed black line) partition function.
References
T. Angelescu et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res., vol. 345, 2, pp. 303-307, 1994
U. Bitelli and F.P. Martins, Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 39, pp. 39-43, 2009
M. Cagnazzo et al., 23rd International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe, 2014